AI Assistant: 5 Steps to a Successful Implementation

With the rise of artificial intelligence, especially natural language processing (NLP), virtual assistants have seen an unexpected boost. Their role is becoming crucial in marketing and sales, as they can competently guide, recommend, and encourage users to take action—across multiple languages and even outside of business hours.
The benefits for organizations are clear: satisfied users and higher conversion rates. However, to make the project successful, users must also see value in using the assistant. Whether they’re looking for a product in an online store, a loan on a banking site, or vacation offers on a travel agency portal—they will only turn to an AI assistant if it:
These goals should guide your approach to introducing an AI assistant on your organization’s website. Simply implementing a generic bot like ChatGPT is not enough. Ask yourself:
Once you have a clear vision of the assistant’s role in your processes, it’s time to begin implementation. Below are five key factors for a successful project:
A virtual assistant offers a unique opportunity to give your website a "human face" and create a more personal relationship with users. You can design a visual persona for the assistant and define its tone of communication.
The assistant can provide customer support, handle routine tasks, help users find specific products, or drive sales. Based on the role you assign to it, you should design appropriate user scenarios that may span multiple platforms and devices.
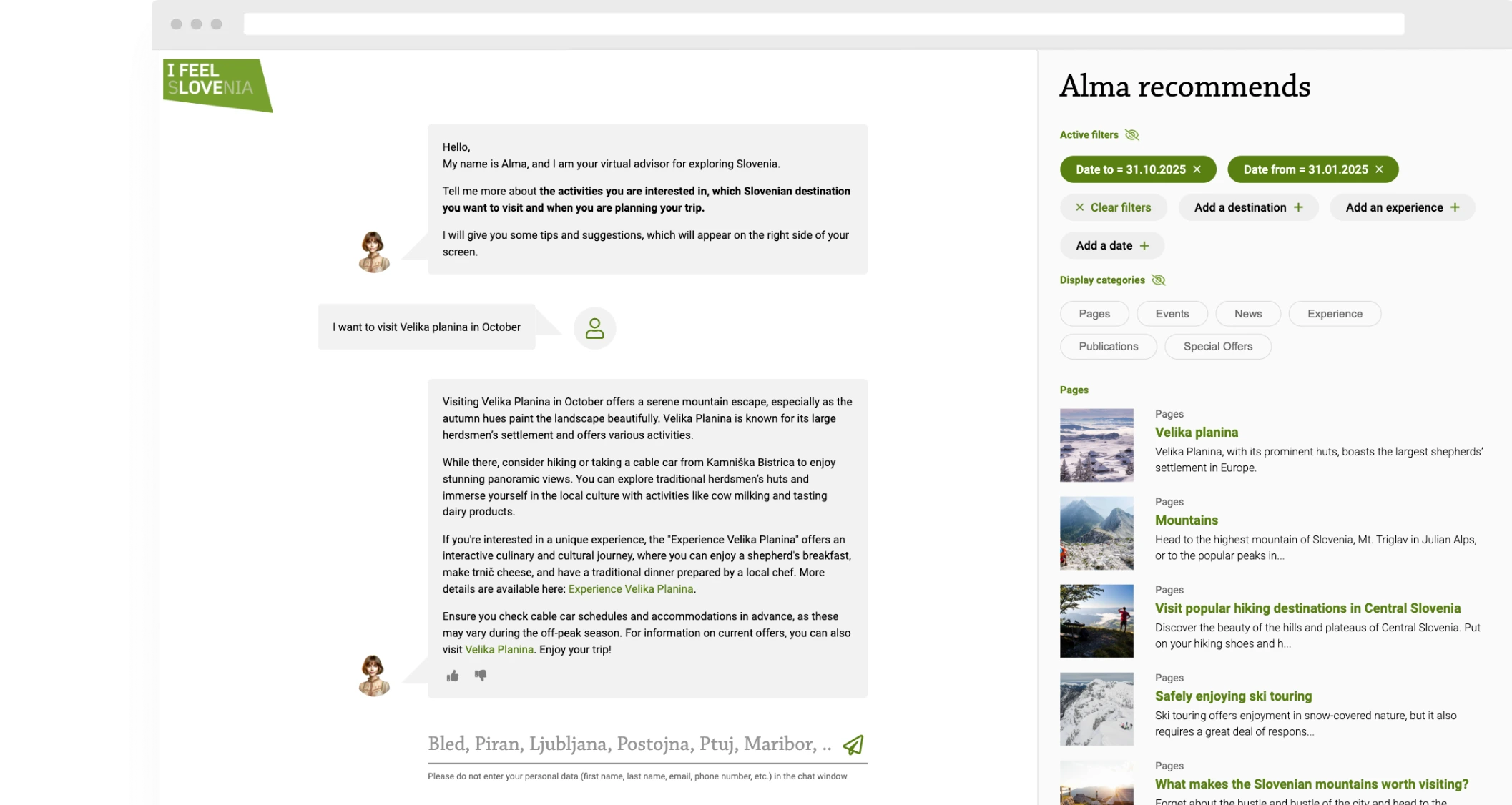
Case Study: Alma, the Virtual Traveler
Alma is an AI-powered virtual assistant on the Slovenia.info portal, where she provides international visitors with relevant information and encourages them to visit Slovenia.
Depending on your company’s AI strategy and project requirements, you’ll need to choose the right platform. There are many free models available that provide basic functionality, which is often enough for simple use cases.
Paid versions give access to the latest algorithms, regular updates, better integration options, and technical support. They also allow for more complex interactions with fewer limitations—such as longer, more nuanced conversations. Although there’s a cost (usually based on the number of queries), prices are dropping and becoming more affordable—for example, just a few dozen euros a month for a bot in five languages.
Designing the assistant’s "context" (i.e., its instructions and behavioral logic) is at the heart of model development. Through trial and error across multiple iterations, we optimize the assistant’s responses for maximum relevance. The faster the assistant understands the user’s intent, the quicker it can provide useful answers.
Generic virtual assistants like OpenAI’s ChatGPT or Google’s Gemini pull data from public online sources, which may not always be accurate or up to date.
Your users expect reliable, real-time information about your products and services. That’s why it’s best to feed the AI assistant from your own data sources—sources you know are trustworthy. You'll also need to define clear guidelines to separate public content from business-sensitive information. Data modeling is, therefore, a critical part of the implementation process.
When integrating a virtual assistant into your website, data privacy and security are paramount. Since data is often processed on servers outside the EU, it should be encrypted before transfer to limit access to personal information.
AI service providers generally follow GDPR and best practices for data protection, but it’s your responsibility to implement safeguards to protect users.
AI thinks independently, and no matter how well the assistant is configured, it will never be 100% reliable. That's why it's essential to continuously monitor and filter its responses.
At Creatim, we work with clients to supervise the assistant’s behavior, filter out unwanted answers, and regularly update its models—ensuring that the output remains accurate, objective, and helpful.
It's not enough to simply add a virtual assistant to your website. You need to ensure it provides real value—offering specific information users wouldn’t easily find elsewhere, or saving them time and effort.
Many virtual assistants on the market are just ChatGPT in a new skin, offering little added value. ChatGPT is a generic product with limited control over its responses.
If you're considering developing a virtual assistant, Creatim can help you make it truly effective. We’ll build it on your data sources—critical if you want users to see it as genuinely helpful and trustworthy.